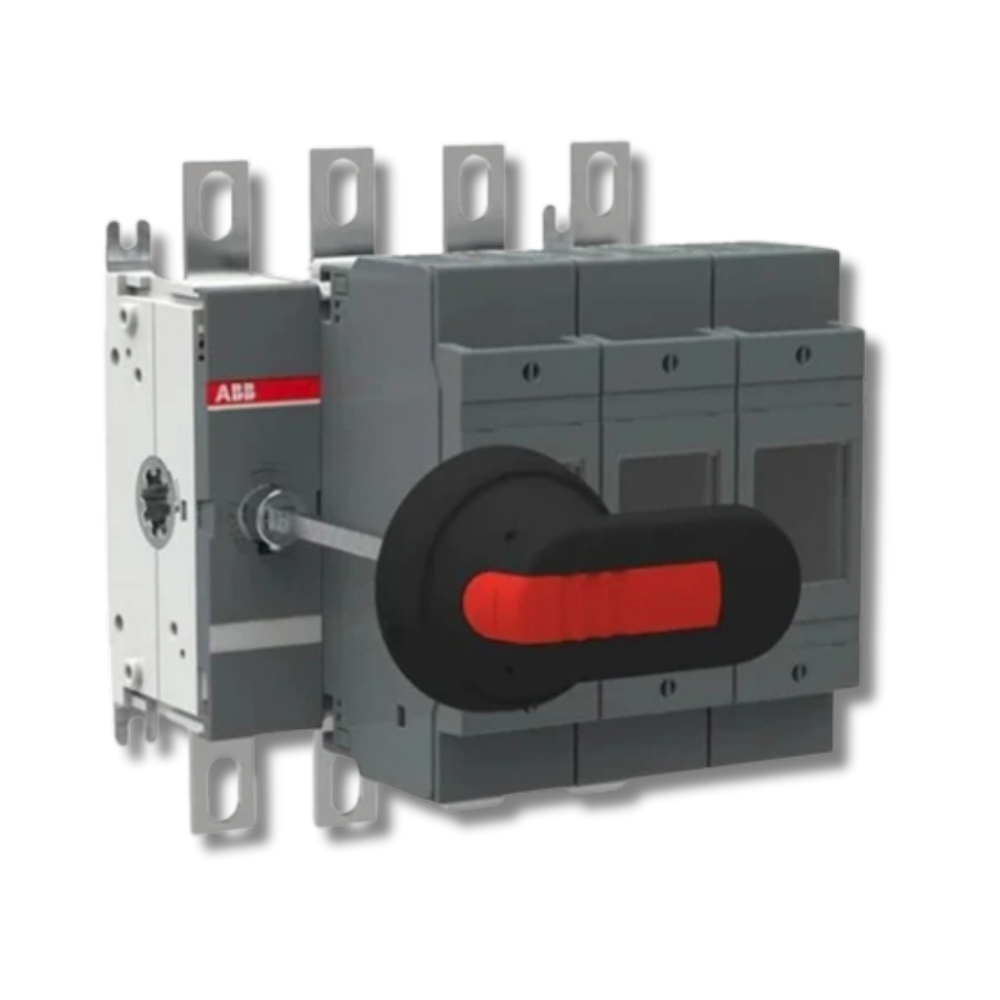
The ABB NAL/NALF Load Break Switch (a.k.a. “FN Switch”) is a modular, indoor-rated switch disconnector designed for high-voltage applications. It excels in providing clear, safe isolation for maintenance and operational control in switchgear, compact substations, and reactive power systems. Its robust design, accessory compatibility, and high interruption rating make it a reliable choice for modern electrical installations.
ABB Group+1
Description
This device is a Load Break Switch, also known as a Switch Disconnector. It’s designed to safely interrupt and isolate electrical loads—particularly useful in motor control centers, capacitor banks, and distribution panels. ABB’s version commonly aligns with their NAL/NALF indoor air-insulated models.
ABB Group
Specifications
Based on ABB’s NAL/NALF indoor load break switch series:
-
Voltage: Up to 36 kV (medium voltage indoor use)
-
Current: Up to 1,250 A
-
Rated short-circuit withstand: Typically up to ~31.5 kA for 1 second
-
Configurations: 3-pole with modular structure
ABB GroupJGGY Electrical
Features
-
Compact, modular design suitable for switchgear and compact substations
-
High number of switching operations at rated current
-
Optional accessories include shunt trip, motor operators, auxiliary contacts, and earthing switches
-
Can be combined with current-limiting fuses for full overcurrent protection (e.g., NALF version)
-
Capable of handling frequent switching and fault condition brief disconnection
ABB GroupJGGY Electrical
Applications
-
Indoor medium voltage switchgear panels
-
Transformer protection via switch-fuse combination
-
Capacitor bank switching, especially in APFC systems
-
Compact substations, motor control centers, and industrial distribution boards
ABB Group+1
Advantages
-
Safely handles load currents, including fault conditions when used with fuses
-
Highly reliable for frequent operation
-
Space-efficient, flexible configuration
-
Facilitates visible isolation and safe maintenance
Disadvantages
-
Manual operation only—no automatic switching
-
Higher voltage-rated models may require specialized installation
-
On its own, it doesn’t provide full overcurrent protection unless paired with fuses or breakers