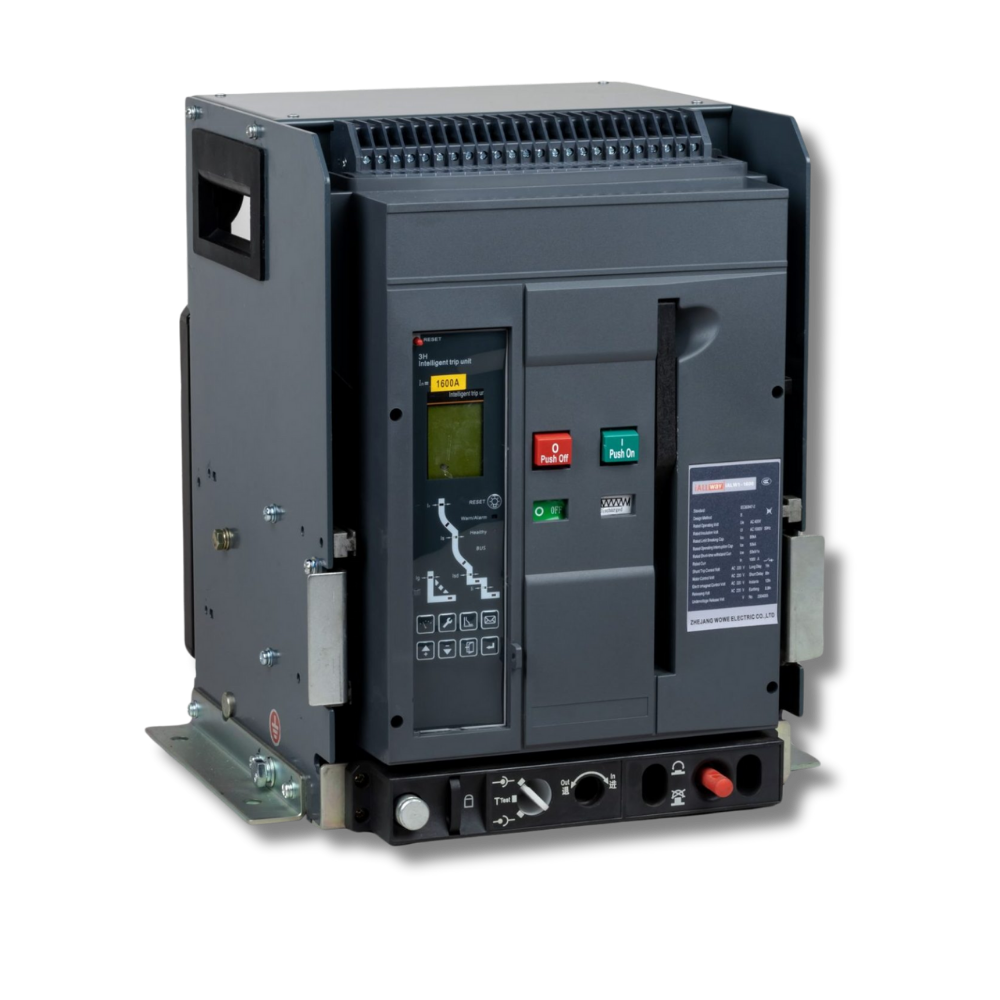
An Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) is a low-voltage protection device that safeguards electrical systems from overload, short-circuit, and earth faults. Operating in air as the arc extinguishing medium, ACBs are widely used in LV panels, transformers, and industrial power distribution up to 690 V and 6,300 A.
Description
An Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) is a type of circuit breaker that operates in the air (at atmospheric pressure) as the arc extinguishing medium. It is used for low-voltage (LV) applications, typically up to 690 V AC and 6,300 A. ACBs provide overload, short-circuit, and earth fault protection and can also be used as a main incoming circuit breaker in LV panels.
Specifications
-
Voltage Rating: Up to 690 V AC (low voltage applications)
-
Current Rating: 630 A to 6,300 A
-
Breaking Capacity: 50 kA to 100 kA (depending on model)
-
Poles: 3-pole / 4-pole
-
Operating Mechanism: Manual (spring-charged) / Motorized
-
Standards: IEC 60947-2
Features
-
Arc Quenching in Air: No special medium required, easy maintenance
-
Multiple Protections: Overload, short-circuit, earth fault, under-voltage
-
Flexible Installation: Fixed type or draw-out type
-
Advanced Versions: Microprocessor-based trip units with communication (Modbus, Ethernet)
-
High Breaking Capacity: Ensures reliable protection in LV distribution
Applications
-
Main incoming breaker in LV switchgear panels
-
Power distribution in industrial plants, commercial complexes, and data centers
-
Backup protection for transformers, generators, and large motors
-
Used in utility substations for LV systems
Advantages
-
Simple design and reliable operation
-
High breaking and making capacity
-
Easy to install and maintain
-
Can be motorized for remote operation
-
Available with advanced electronic trip units
Disadvantages
-
Bulky size compared to MCCB or MCCB alternatives
-
Limited to low-voltage applications (not suitable for >1 kV)
-
Higher cost compared to MCCBs in smaller ratings
-
Requires regular inspection due to air as arc medium