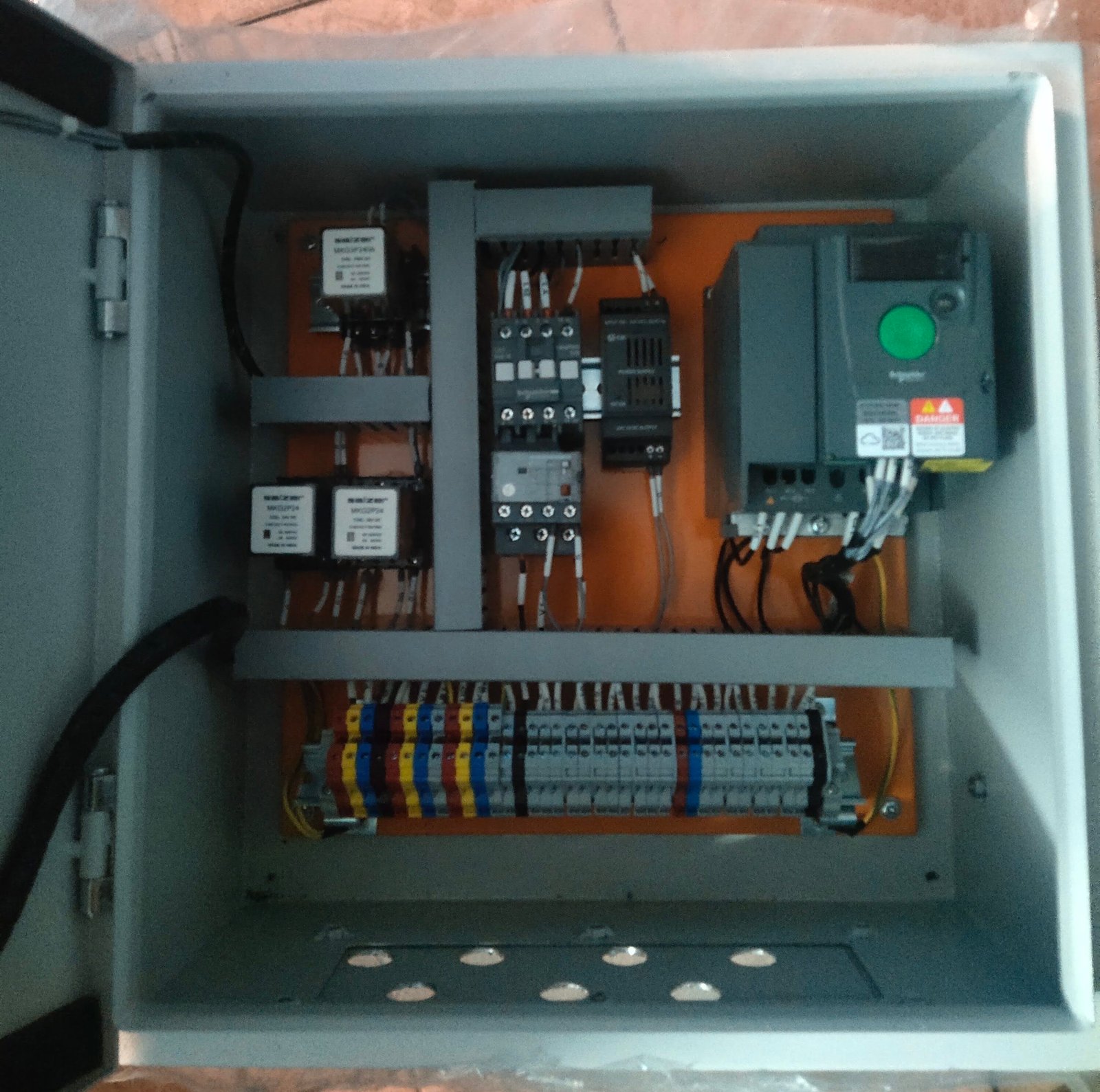
Fuses and Fuse Links are essential protective devices used to safeguard electrical circuits from overcurrent and short circuits. A fuse contains a metal element that melts when current exceeds safe levels, interrupting the circuit. Fuse links are the replaceable elements inside fuses, ensuring cost-effective and easy maintenance. Widely used in power distribution, industrial equipment, automotive, and household systems, they provide reliable protection, compact design, and quick fault response.
Description
Fuses and Fuse Links are critical electrical protection devices designed to prevent damage caused by overloads and short circuits. A fuse interrupts excessive current flow by melting its internal element, while a fuse link is the replaceable melting element housed inside the fuse body. Together, they ensure safety, reliability, and cost-effective maintenance in electrical and electronic systems.
Specifications
-
Types of Fuses: Cartridge fuses, HRC (High Rupturing Capacity) fuses, Blade fuses, Thermal fuses, Resettable fuses
-
Fuse Link Types: Standard fuse link, High-speed fuse link, Automotive fuse link, Solar PV fuse link
-
Current Rating: From milliamps (mA) to several kiloamperes (kA)
-
Voltage Rating: Low voltage (LV), Medium voltage (MV), High voltage (HV) options
-
Breaking Capacity: From few kA up to 120kA (depending on type)
-
Standards Compliance: IEC 60269, UL 248, BS 88, IS standards
-
Construction Material: Ceramic, glass, plastic, silver/copper fuse element
Applications
-
Power distribution panels and switchgear
-
Industrial machinery and control systems
-
Automotive electrical systems (cars, trucks, EVs)
-
Renewable energy systems (solar PV, wind, battery storage)
-
Consumer electronics and household appliances
-
Transformers and motor protection
Advantages
-
Provides fast and reliable overcurrent protection
-
Simple, cost-effective, and maintenance-friendly
-
Fuse links make replacement quick and economical
-
Compact size and easy installation
-
Available for wide range of voltage and current ratings
Disadvantages
-
Once blown, fuses must be replaced (not reusable)
-
Incorrect fuse selection can lead to nuisance tripping or insufficient protection
-
Requires spare fuse links for uninterrupted operation