A Line Reactor is an essential protective device for modern electrical and automation systems. By reducing harmonics, voltage surges, and electrical noise, it ensures reliable performance of VFDs, inverters, and sensitive equipment. With different impedance options (1%, 3%, 5%), line reactors are a proven solution for extending the life of industrial power electronics and improving overall power quality.
Description
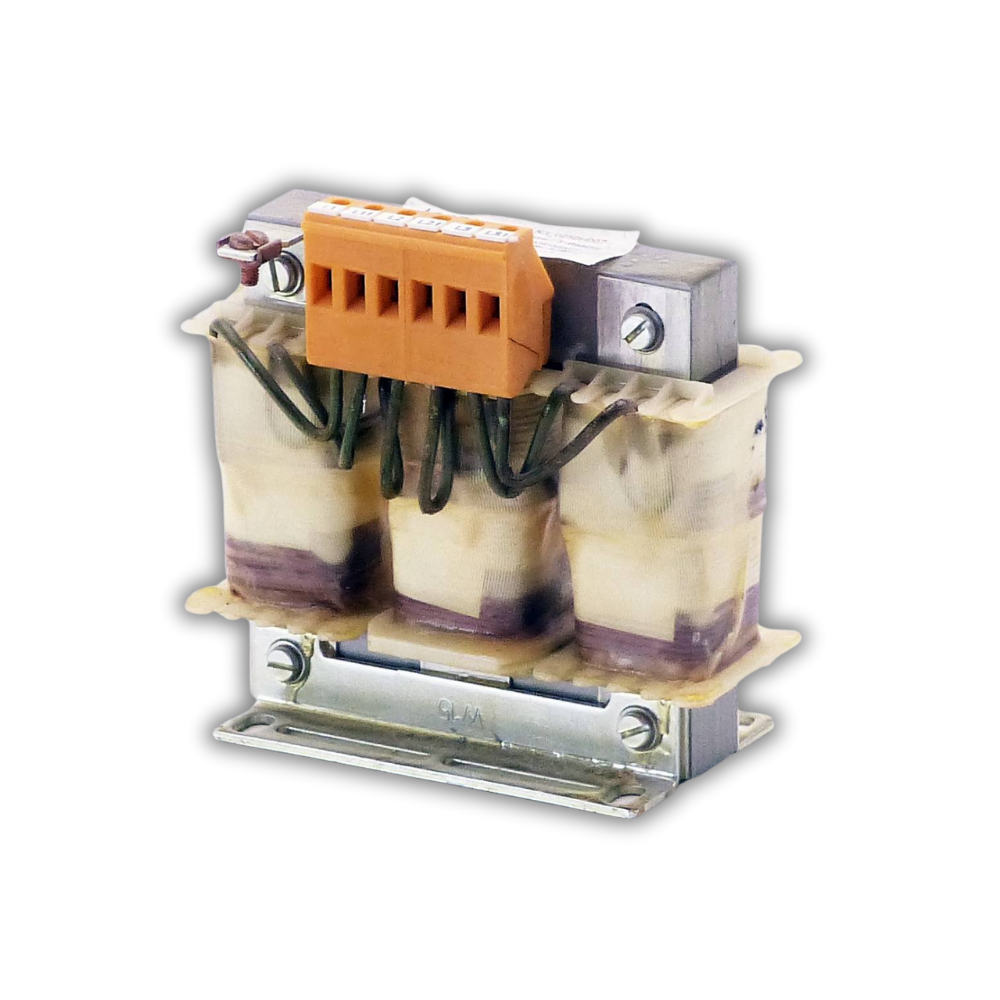
A Line Reactor (also known as an AC Reactor or Input Reactor) is an inductive device installed at the input of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), inverters, or other sensitive equipment to limit harmonics, reduce inrush current, and protect against voltage spikes. It improves power quality, extends the life of drive components, and ensures smoother operation of electrical systems.
Specifications
-
Type: 3-Phase / Single-Phase Line Reactor
-
Input Voltage: 230V / 415V / 690V AC (depends on rating)
-
Current Rating: 1A to 1000A (or custom as per application)
-
Inductance Value: 1% / 3% / 5% impedance reactors
-
Frequency: 50Hz / 60Hz
-
Cooling: Natural Air Cooled (AN)
-
Insulation Class: Class F / H
-
Mounting: Panel / Floor / Enclosure-based
-
Standards: IEC 60076 / IS 5553 compliant
Features
-
Reduces harmonics and line notching
-
Limits inrush and short-circuit currents
-
Protects VFDs, inverters, and other power electronics
-
Improves power factor and overall system reliability
-
Extends lifespan of semiconductors and capacitors in drives
-
Available in both 1-phase and 3-phase versions
-
Compact, robust, and easy to install
Applications
-
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) & Servo Drives
-
UPS systems and inverters
-
CNC machines and robotics
-
HVAC systems and elevators
-
Renewable energy systems (solar/wind)
-
Industrial automation panels
-
Power distribution networks
Advantages
-
Protects drives from transients, surges, and spikes
-
Reduces harmonic distortion in power lines
-
Enhances reliability and service life of equipment
-
Improves system stability during voltage fluctuations
-
Provides better motor performance with smoother current flow
Disadvantages
-
Adds cost to the installation
-
Occupies space in control panels or distribution rooms
-
May cause a small voltage drop across the line