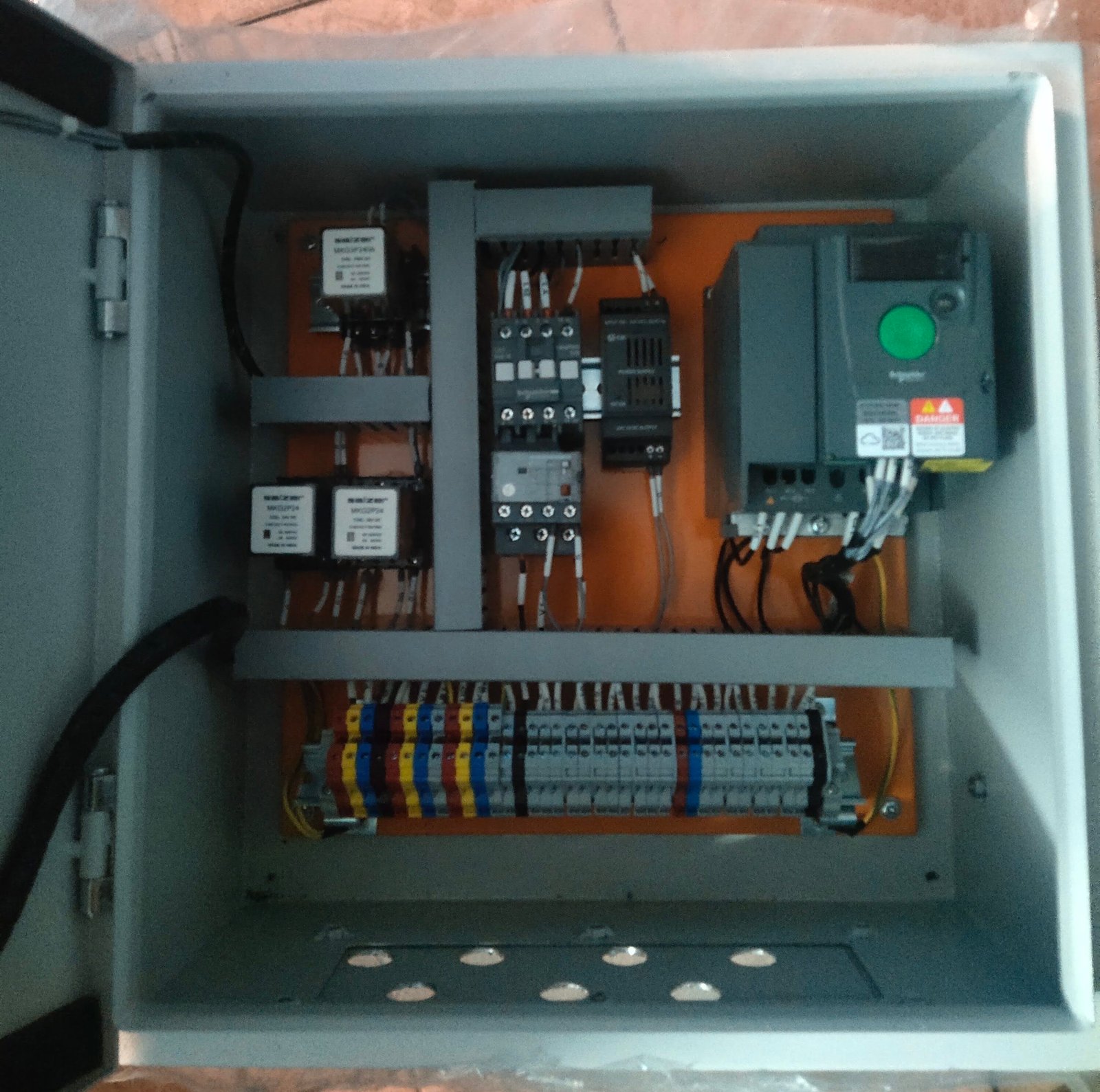
A Relay Module is an essential switching device that allows low-power control signals to operate high-voltage or high-current loads safely. Designed with electromagnetic or solid-state relays, these modules provide electrical isolation between control and power circuits, ensuring reliable and secure operation. Widely used in automation, home control, industrial machinery, and microcontroller projects, relay modules offer versatile, cost-effective, and durable solutions for switching applications.
Description
A Relay Module is an electronic switching device that uses an electromagnetic relay to control high-voltage or high-current loads with a low-power signal. Commonly used with microcontrollers, PLCs, and automation systems, relay modules provide electrical isolation between control and load circuits, ensuring safe and reliable operation. Available in single-channel or multi-channel versions, they are widely used in industrial, commercial, and DIY automation applications.
Specifications
-
Type: Electromechanical / Solid-State Relay Module
-
Channels: 1, 2, 4, 8, or more (depending on model)
-
Control Voltage: 3.3V DC / 5V DC / 12V DC / 24V DC
-
Load Voltage: AC 110V – 250V or DC 0–30V (varies by type)
-
Load Current: Typically 10A per channel (higher capacity available)
-
Isolation: Optocoupler isolation for safety (in most models)
-
Mounting: PCB mount / Screw terminal / DIN rail (industrial type)
-
Protection: LED indicators, overvoltage, and surge protection (model dependent)
Applications
-
Industrial automation and process control
-
Home automation and smart devices
-
PLC and microcontroller projects (Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ESP32, etc.)
-
Motor, pump, and solenoid control
-
Lighting and HVAC systems
-
Renewable energy and power distribution panels
Advantages
-
Allows low-power devices to control high-power loads
-
Provides electrical isolation for system safety
-
Available in multiple channel configurations
-
Easy to interface with microcontrollers and PLCs
-
Cost-effective and versatile switching solution
Disadvantages
-
Mechanical relays have limited switching life (wear and tear)
-
Slower switching speed compared to solid-state relays
-
Generates noise (clicking sound in mechanical relays)
-
Requires proper driver circuitry for high-current loads