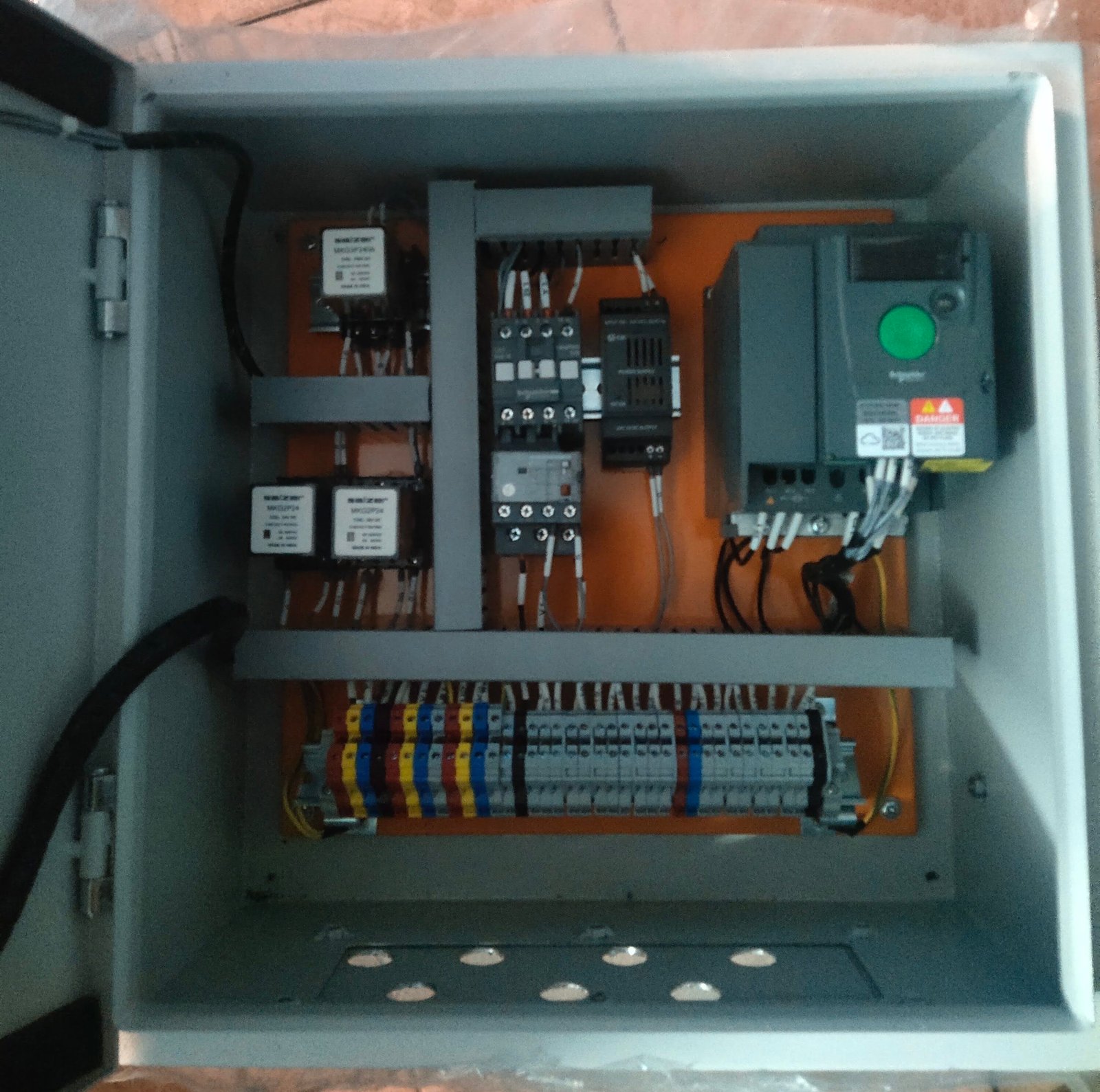
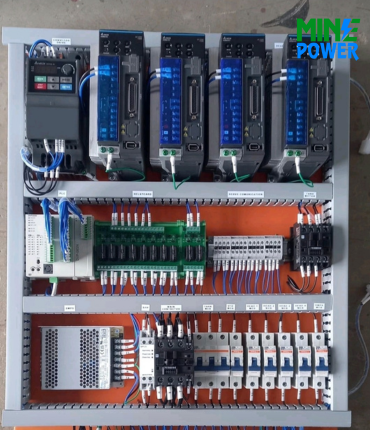
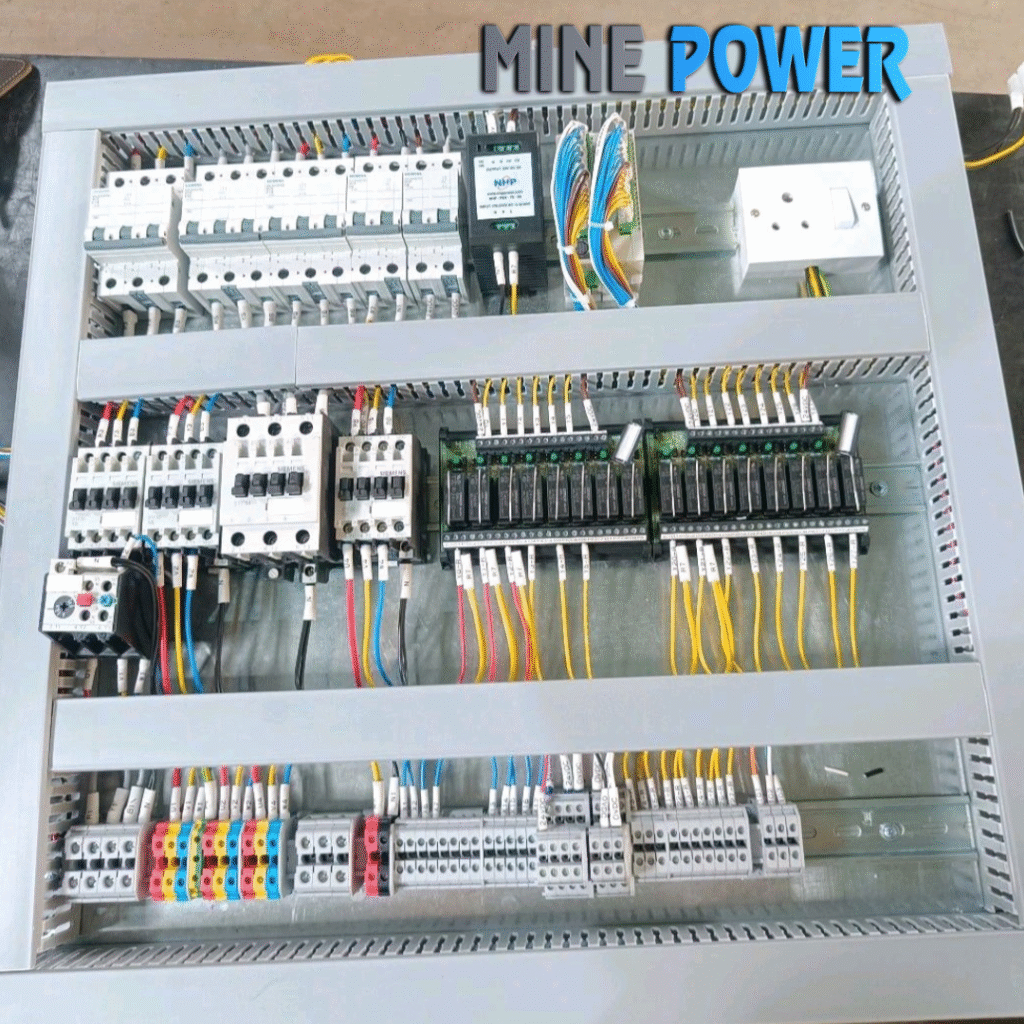
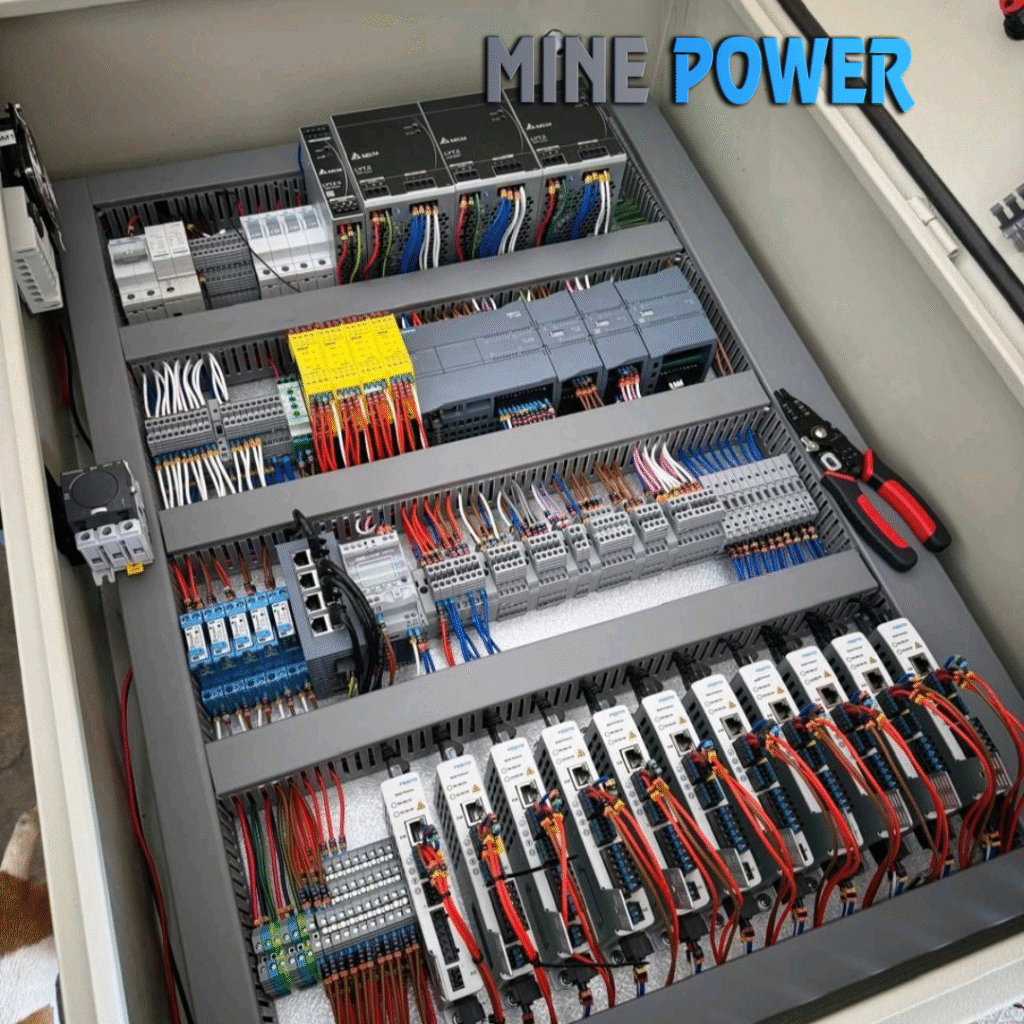
Safety switches are essential protective devices used to isolate electrical circuits and ensure safe operation during maintenance, repairs, or emergency conditions. Designed to disconnect power quickly and reliably, they safeguard both people and equipment from electrical hazards such as shocks, arc flashes, and accidental startups. Available in fused, non-fused, emergency stop, and interlock types, safety switches are built with rugged enclosures, visible contact indication, and lockable handles for added security. They are widely used across industrial plants, commercial facilities, motor control centers, renewable energy systems, and HVAC applications, making them a critical part of modern electrical safety and compliance standards.
Description
A Safety Switch is an electrical device designed to quickly disconnect power in case of faults or maintenance needs, protecting both people and equipment. Unlike regular switches, safety switches provide visible isolation and often include padlock features to prevent accidental re-energization.
Specifications
-
Voltage Rating: 240V / 415V / 690V AC, 24V / 1000V DC (for solar/industrial use)
-
Current Rating: 16A – 630A+
-
Poles: 1P, 2P, 3P, 4P
-
Standards: IEC 60947-3, UL 98
-
Enclosure: IP54 / IP65 (dust & water protection)
-
Mounting: Wall mount, panel mount, door interlock
-
Type:
-
Fused Safety Switch
-
Non-Fused Safety Switch
-
Emergency Stop Safety Switch
-
Interlock Safety Switch
-
Features
-
Quick and reliable ON/OFF isolation
-
Padlockable handles for safe maintenance
-
Visible contact indication for operator safety
-
Available in fused and non-fused versions
-
Rugged enclosures with IP-rated protection
-
Compact and easy to install
Applications
-
Industrial machines and conveyors
-
Power distribution systems
-
Motor control centers (MCCs)
-
Renewable energy (solar DC isolators, wind turbines)
-
HVAC, elevators, and heavy-duty equipment
-
Emergency shutdowns in hazardous areas
Advantages
-
Ensures safe disconnection during faults
-
Protects personnel from electrical hazards
-
Enhances system reliability
-
Reduces risk of accidental startup
-
Meets safety compliance standards
Disadvantages
-
Adds extra cost compared to standard switches
-
Requires manual operation (unless automated type)
-
Needs regular inspection for mechanical wear
-
Not a replacement for circuit breakers (no advanced fault protection in non-fused types)