A temperature sensor integrated with a PLC enables precise monitoring and control of industrial processes by converting heat variations into electrical signals. Widely used in manufacturing, HVAC, food, and pharmaceuticals, it ensures accuracy, safety, and efficiency in automation systems.
Description
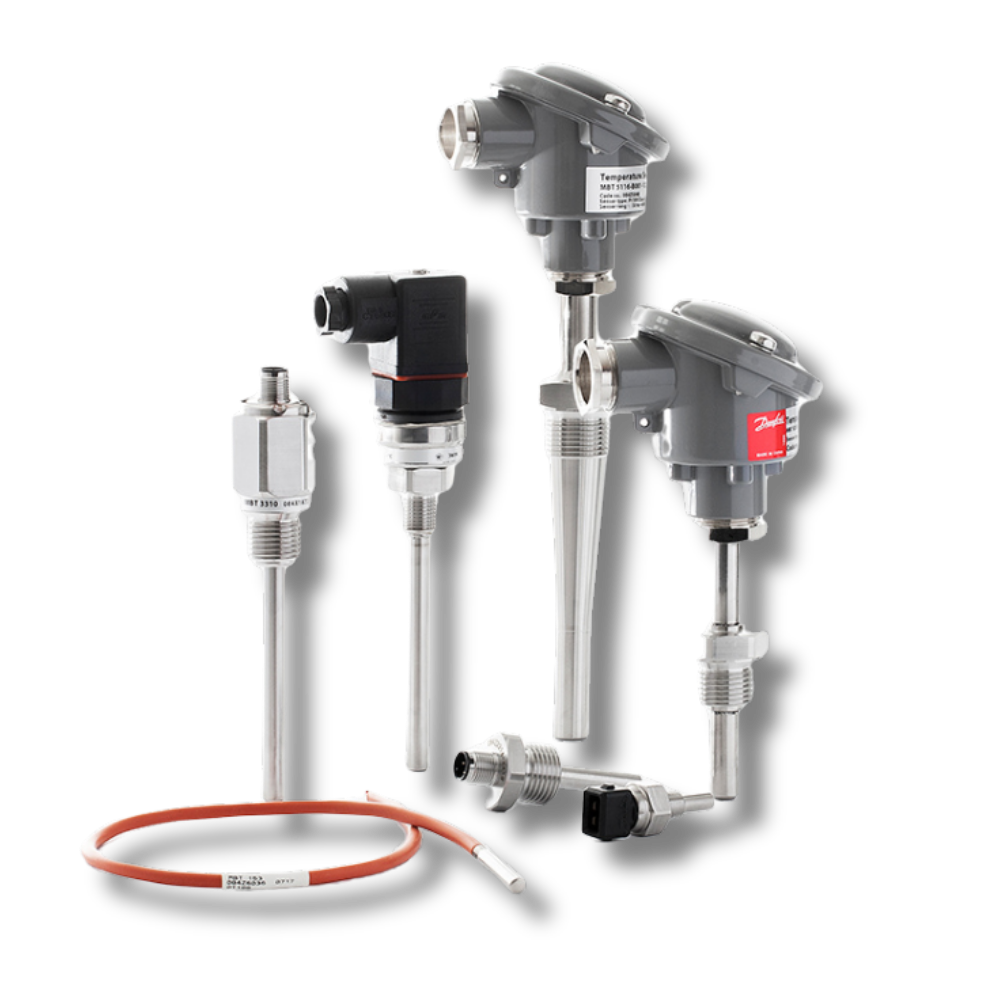
A temperature sensor is a device that detects temperature changes and converts them into electrical signals. When connected to a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), it enables automated monitoring and control of heating, cooling, and process operations. Temperature sensors are essential in industries like manufacturing, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and HVAC systems for maintaining process accuracy and product quality.
Specifications
-
Types: Thermocouple, RTD (Pt100/Pt1000), Thermistor, Infrared sensor
-
Measuring Range: -200°C to +1200°C (varies with type)
-
Accuracy: ±0.1°C to ±2°C (depending on sensor type)
-
Output: mV (Thermocouple), Ω (RTD), Resistance (Thermistor), 4–20 mA / 0–10 V (conditioned signal)
-
Response Time: <1 second to few seconds
-
Interface with PLC: Analog input module or dedicated temperature module
-
Material: Stainless steel sheath / protective casing
-
Operating Environment: Industrial, harsh, or hygienic conditions depending on design
Key Features
✅ High accuracy and sensitivity
✅ Wide operating range (cryogenic to high-temperature applications)
✅ Compatible with most PLC brands (Siemens, Allen-Bradley, Mitsubishi, etc.)
✅ Fast response time for dynamic processes
✅ Long service life with protective housings
✅ Easy integration with analog/digital PLC modules
Applications in PLC Systems
-
Industrial Furnaces & Boilers (temperature monitoring & control)
-
HVAC Systems (heating, ventilation, cooling automation)
-
Food & Beverage Industry (pasteurization, cooking, storage monitoring)
-
Pharmaceutical Industry (clean rooms, production monitoring)
-
Plastic & Chemical Processing (temperature-dependent reactions)
-
Automotive Industry (engine testing, process heating)
Advantages
✔ Accurate and reliable temperature measurement
✔ Enables process automation and safety control
✔ Wide variety of sensors for different applications
✔ Reduces human monitoring efforts
✔ Supports energy-efficient operation
Disadvantages
✖ Different sensor types need different conditioning circuits
✖ Sensitive to electrical noise if not shielded properly
✖ May degrade under extreme mechanical stress or corrosion
✖ Requires calibration for precise applications