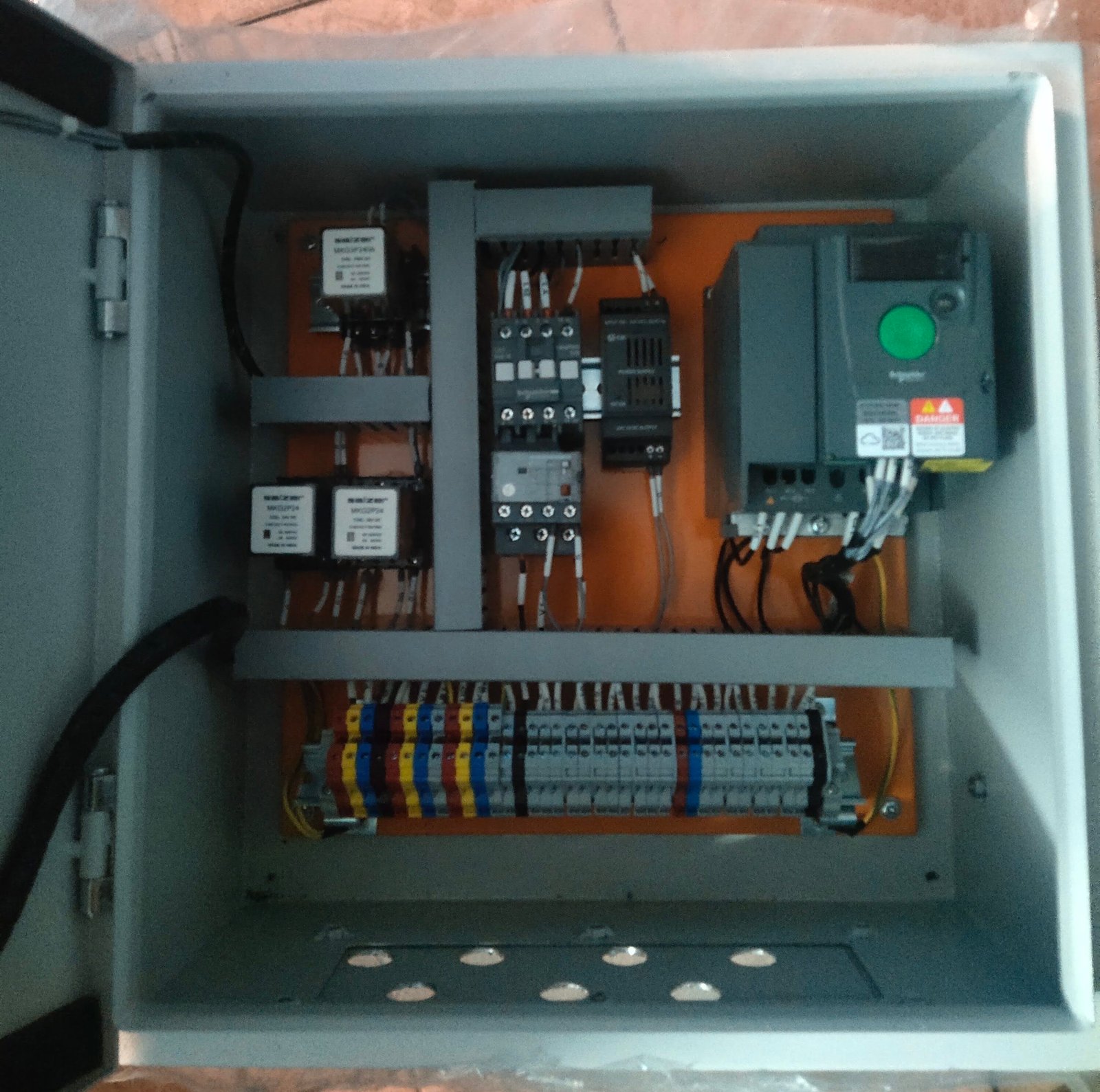
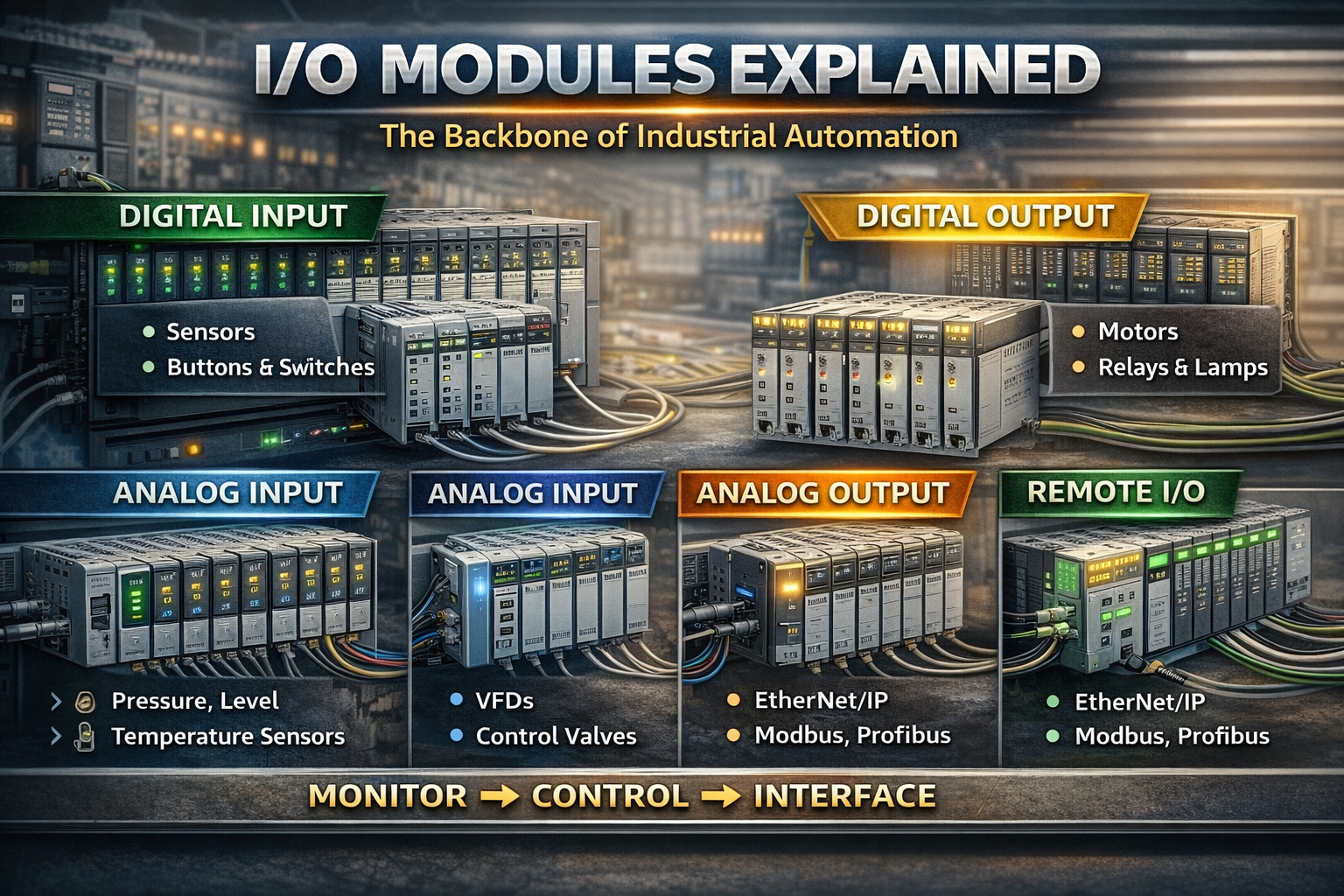
Types of I/O Modules in Industrial Automation
1. Digital Input (DI) Modules
Digital input modules read ON/OFF signals from field devices.
Common inputs:
-
Push buttons (Start / Stop)
-
Proximity sensors
-
Limit switches
-
Selector switches
Signal levels:
-
24V DC (most common)
-
110V AC / 230V AC (industrial panels)
Example:
If a proximity sensor detects a product, the DI module sends a logic “1” to the PLC.
2. Digital Output (DO) Modules
Digital output modules send ON/OFF commands from the PLC to field devices.
Common outputs:
-
Contractors
-
Solenoid valves
-
Indicator lamps
-
Relays
Output types:
-
Relay output
-
Transistor output
-
Triac output
Example:
When PLC logic turns ON a motor, the DO module energizes a contactor.
3. Analog Input (AI) Modules
Analog input modules read continuous signals from instruments.
Typical signals:
-
4–20 mA
-
0–10 V
-
RTD / Thermocouple (with dedicated modules)
Common instruments:
-
Pressure transmitters
-
Temperature sensors
-
Flow transmitters
-
Level sensors
Example:
A pressure transmitter sends 12 mA, which the PLC interprets as a specific pressure value.
4. Analog Output (AO) Modules
Analog output modules send variable control signals to devices.
Applications:
-
Speed control of VFDs
-
Valve position control
-
Heater power regulation
Example:
PLC sends 6 mA to control a valve at 30% opening.
Local I/O vs Remote I/O Modules
Local I/O
-
Installed inside the PLC panel
-
Short wiring distance
-
Suitable for small machines
Remote I/O
-
Installed near-field devices
-
Communicates via protocols like
-
Modbus
-
Profibus
-
Profinet
-
Ethernet/IP
-
Advantages:
-
Reduced cable cost
-
Faster installation
-
Better scalability
Why I/O Modules Are Critical for Machine Reliability
Proper selection and wiring of I/O modules ensures:
-
Accurate signal reading
-
Fast response time
-
Reduced noise and signal loss
-
Improved machine safety
-
Easier troubleshooting
Faulty or poorly selected I/O modules can cause:
-
False signals
-
Unexpected machine trips
-
Production losses
Common Industrial Applications of I/O Modules
-
Manufacturing automation
-
Power distribution panels
-
Water and wastewater treatment
-
Packaging machines
-
CNC and material handling systems
-
Process industries (chemical, pharma, cement)
Best Practices for Using I/O Modules
-
Match signal type correctly (AC/DC, analog range)
-
Provide proper grounding and shielding
-
Use separate power supplies for field I/O
-
Label I/O clearly in drawings and panels
-
Monitor I/O status via PLC or SCADA
Conclusion
I/O modules are the foundation of any PLC automation system. Whether digital or analog, local or remote, these modules ensure seamless communication between machines and control logic.
Understanding I/O modules helps engineers design reliable, scalable, and safe automation systems, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.