PLC Programming and Ladder Logic: A Deep Dive into Industrial Automation
Introduction: Why PLC Programming and Ladder Logic Matter
PLC Programming and Ladder Logic are the backbone of modern automation. Every conveyor belt, robotic arm, and traffic system depends on them to run safely and efficiently. Without PLCs, industries would struggle to control machines with the precision and reliability required today.
At Mine Power, we believe that understanding PLC Programming and Ladder Logic means going beyond the basics and diving into the hidden details that make PLCs the true brains of industry.
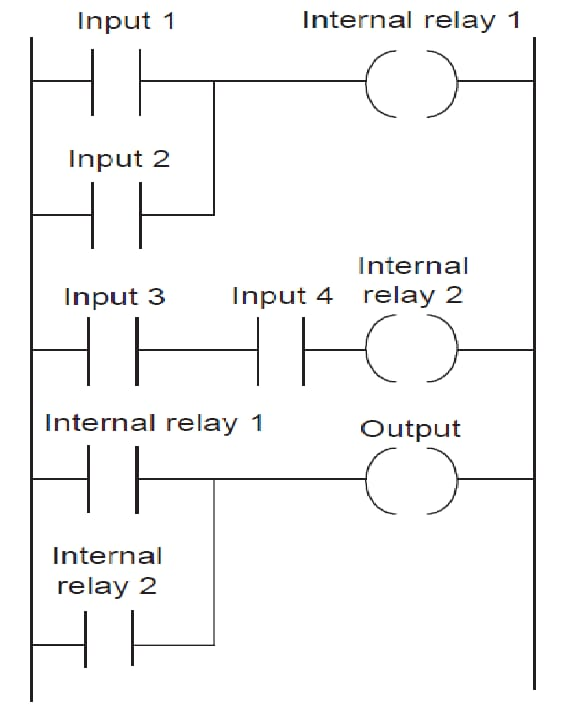
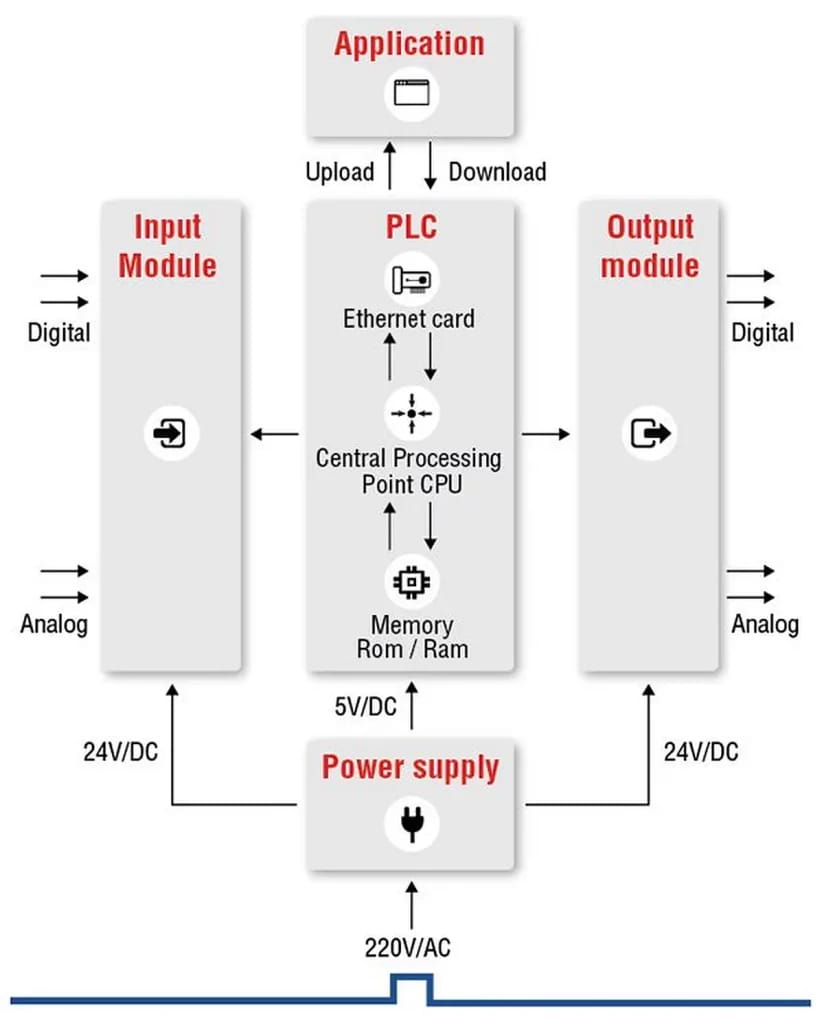
PLC Programming and Ladder Logic in the Scan Cycle
Every PLC operates in a repeating scan cycle, usually measured in milliseconds:
-
Input Scan – Detects sensor and switch states.
-
Program Scan – Executes the logic line by line.
-
Output Scan – Activates motors, valves, and indicators.
-
Housekeeping – Handles communication, memory, and diagnostics.
💡 Unique Fact: A PLC can run through this cycle 1000+ times per second, ensuring that safety systems like emergency stops work .

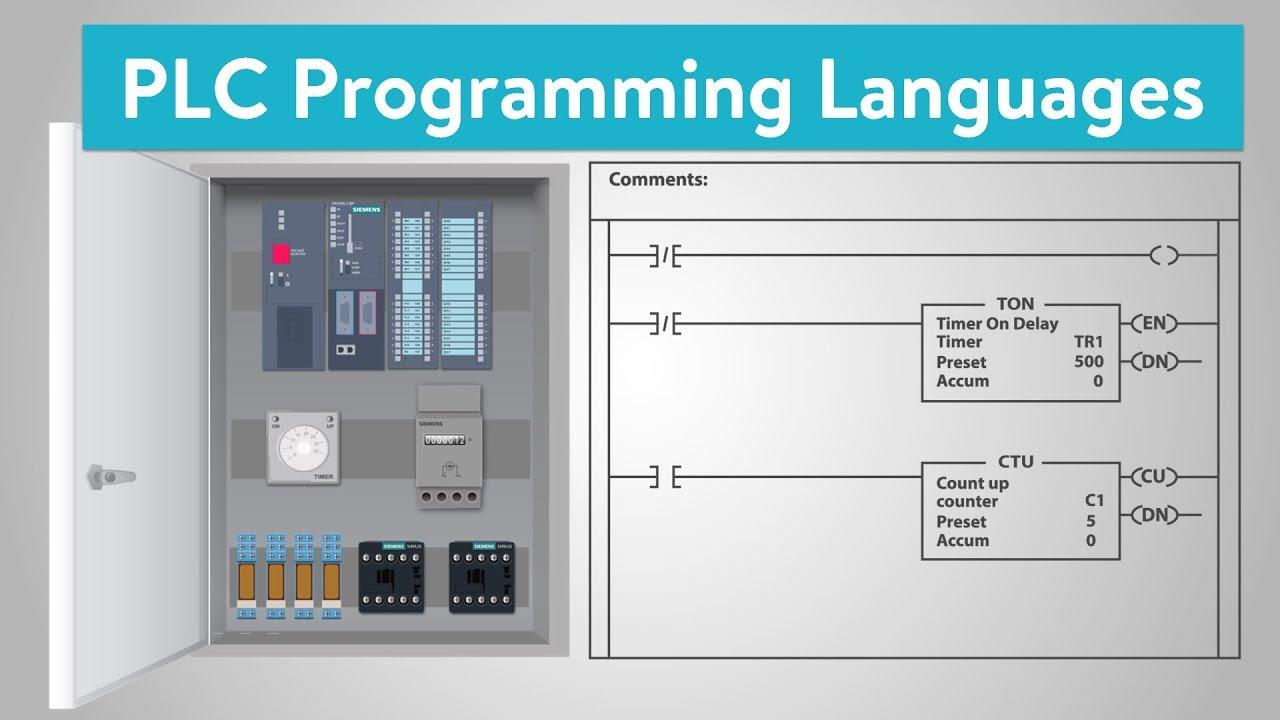
Why Ladder Logic Dominates PLC Programming
Why not just program PLCs with C or Python? The answer lies in industrial history. Electricians and technicians used relay diagrams long before digital programming existed.
Ladder Logic was designed to look like relay circuits, making it familiar and easy for engineers who already understood wiring diagrams.
👉 This is why PLC Programming and Ladder Logic remain the global standard in industries ranging from automotive to food processing.
Beyond ON/OFF: Advanced Functions of PLC Programming and Ladder Logic
Most people think PLCs only switch outputs. In reality, PLC Programming and Ladder Logic allow for:
-
Timers – Delays, flashing lights, and sequencing operations.
-
Counters – Counting bottles, tracking cycles, or monitoring items.
-
Analog Processing – Handling values like temperature, flow, and pressure.
-
PID Control – Precision control of motors, heaters, and pumps.
-
Communication – Exchanging data with SCADA, HMIs, and IoT devices.
💡 Unique Fact: Some advanced PLCs perform motion control for robotics and CNC machines, reducing the need for separate controllers.
Real-World Example: PLC Programming and Ladder Logic in Traffic Control
Imagine a smart traffic system:
-
Inputs: Vehicle sensors, pedestrian push buttons.
-
Logic:
-
If pedestrian button pressed → switch lights for safe crossing.
-
If high traffic detected → extend green light duration.
-
-
Outputs: Red, yellow, and green signals adapt dynamically.
👉 Unlike timer-based systems, PLC Programming and Ladder Logic make real-time adjustments for safety and efficiency.
Challenges in PLC Programming and Ladder Logic
Behind the scenes, engineers must deal with:
-
Scan Time Sensitivity – Missing fast signals in high-speed machinery.
-
Safety First – Interlocks and emergency stops always override logic.
-
Memory Optimization – Efficient coding prevents slowdowns.
-
Redundancy – Critical systems often run two PLCs in parallel for reliability.
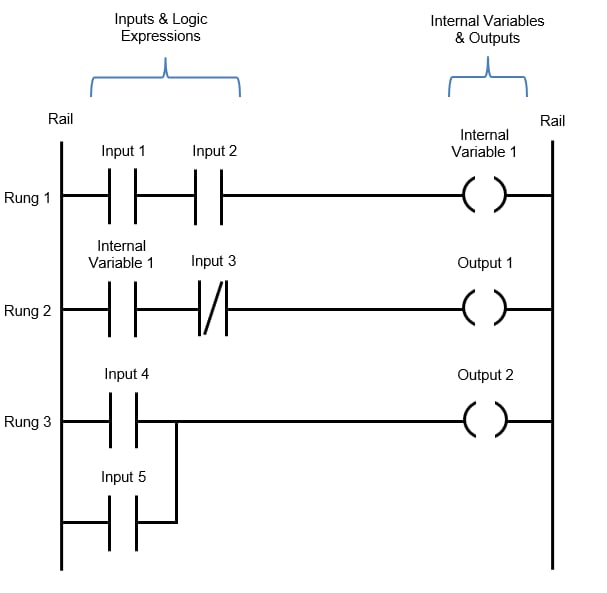
PLC Programming and Ladder Logic: The Future with Industry 4.0
✔ Bridges electrical, mechanical, and software fields.
✔ Every manufacturing, water, energy, and automotive industry needs PLC experts.
✔ Industry 4.0 connects PLC Programming and Ladder Logic with IoT, AI, and cloud systems.
💡 Future Insight: PLCs are evolving into edge computers capable of running machine learning models directly on the factory floor.
Key Takeaway
PLC Programming and Ladder Logic = Industrial Intelligence
-
Not just ON/OFF control – but timing, counting, analog handling, and communication.
-
Reliable because of the scan cycle.
-
Ladder Logic remains dominant because it speaks the language of industry.
At Mine Power, we believe mastering PLC Programming and Ladder Logic transforms an engineer into an automation leader ready for Industry 4.0.
🔗 Our automation services: Mine Power Website